The IVF Process
Pre-cycle Preparation
Our patients will meet with their physician to discuss their diagnosis and develop a treatment plan. During this conversation, their doctor will also review the various tests and fertility medications that they will need prior to the IVF process. After this point, the patient will be assigned to one of our nurse coordinators, who will review their IVF plan, explain their medication schedule and answer any and all questions.
IVF medications
Medications our patients are likely to receive may include birth control pills started in the month before the IVF treatment cycle, and the injectable medication leuprolide (Lupron), started just before finishing the oral contraceptives. Together, these medications prepare a woman for ovulation induction or the releasing of eggs from the ovaries. Alternatively, a physician my recommend a protocol that uses a medication called Cetrotide, taken 10 days after ovulation in the cycle preceding the IVF stimulation cycle or oral estrogen in the last 7 days prior to the IVF cycle. One of our most common protocols does not require any medications prior to the IVF cycle.
Ovulation Induction
IVF literally it means “fertilization in glass,” because the woman’s eggs and the man’s sperm are fertilized in a Petri dish. During the IVF process, a patient’s natural cycle is carefully manipulated through the use of fertility medications. These medications stimulate the ovaries to produce not one, but a number of mature eggs. At the right time, the eggs are retrieved from the ovaries. At this time, the male supplies a sperm sample (or a stored, frozen sample is used). The eggs and sperm are placed in a Petri dish and fertilized. At the proper time, the embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus.
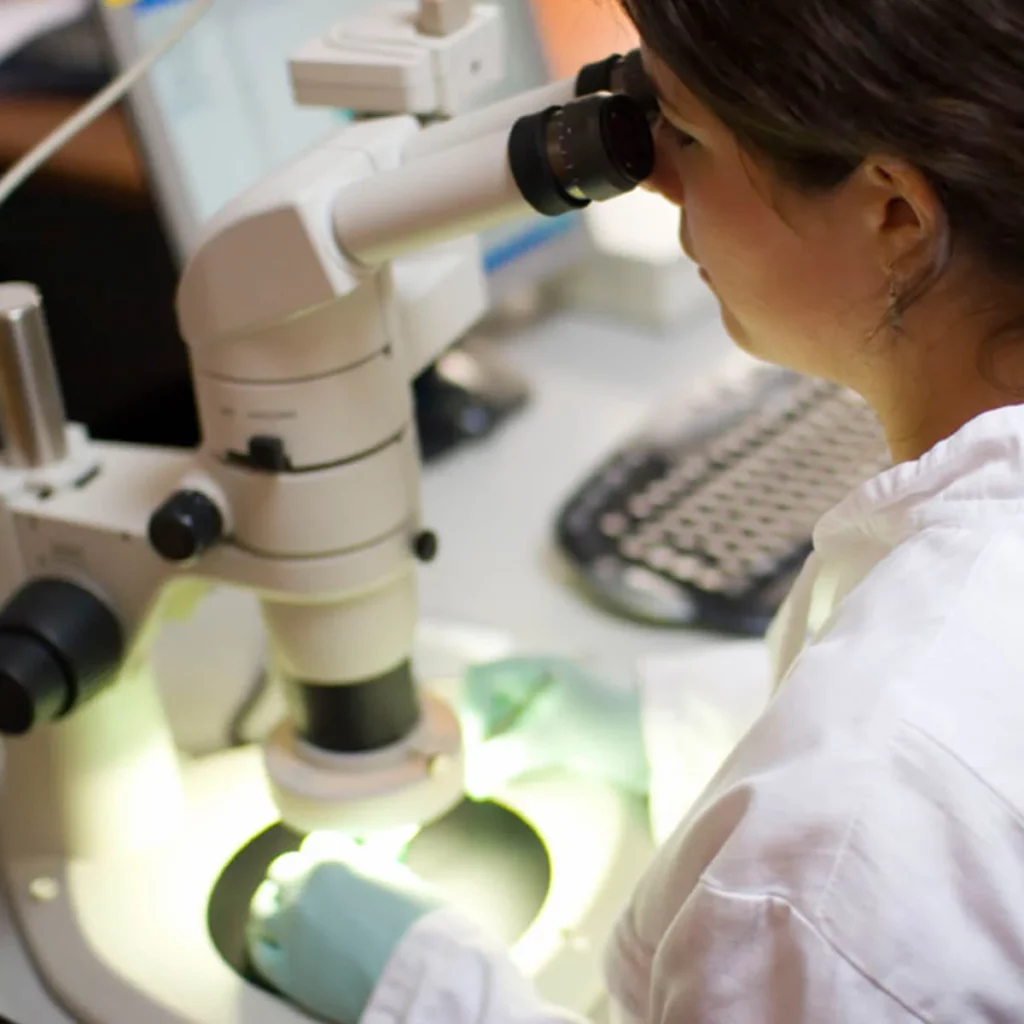
Insemination and Fertilization
Some of the most important events in a cycle now occur behind the scenes, in our laboratory. Eggs mature for a few hours in the incubator and sperm are added. We add about 50,000 to 100,000 motile sperm into each droplet of culture media containing each egg. This is called insemination. Insemination is followed several hours later by fertilization, when the sperm enters the egg.
The embryos now begin dividing in the Petri dish, growing to eight-cells by day three and up to 100 cells by day 5-6 (at this stage, embryos are called blastocysts).
There are a number of procedures that can be done in our lab to enable healthy embryo development. The patient’s doctor will let them know if a given procedure is recommended.
Embryo Culture and Development
Some of the most important events in the IVF treatment cycle now occur behind the scenes, in our laboratory. Our security in handling eggs, sperm and embryos is unusually meticulous. Our laboratory protocol, SurTransferSM (see detailed article in Additional Information section) calls for two of our board certified embryologists to be present at all critical steps to avoid any potential errors.
The eggs mature for several hours in culture media. This media is made up of essential amino acids and other components necessary for good embryo development. The nutrients and sperm are then added to the eggs and media, usually in the afternoon of the egg retrieval. The addition of sperm to the culture media is called insemination. Insemination is followed several hours later by fertilization, when the sperm enters the egg.
The stages that follow are very important to the future embryo. After fertilization, the sperm loses its tail and its head enlarges, so that, at this stage, the egg looks like a cell with two nuclei, called pro-nuclei. The pro-nuclei, which individually hold the genetic material of the sperm and the egg, are called pro-nuclei because each has only half the DNA of a normal nucleus. You may hear this stage referred to as the two pro-nuclear or 2PN stage. Identification of the 2PN stage is very important to determine if fertilization has occurred.
Egg Retrieval
Eggs are removed from the ovaries approximately 36 hours after taking the HCG injection. If the patient regularly take any medications (allergy medication for example) they should talk with their doctor or nurse about taking the medication on the day of the egg retrieval.
The patient will be asked to not eat or drink as of midnight before the egg retrieval. During the egg retrieval procedure, they will receive a mild sedative through an IV, a small tube in a vein in the arm. This is a form of light general anesthesia where they will breathe on their own but will not feel the procedure nor remember it afterwards.
After they are sedated, the vagina is washed with a sterile water solution. A needle is placed under ultrasound guidance into the ovary and fluid, and eggs from the follicles in the ovaries are collected into a test tube and sent to the IVF lab. The whole procedure takes about 30 minutes, and discomfort is generally minimal.

Embryo Transfer
After PGT-A biopsy, all embryos are vitrified (frozen) while we wait 10- 14 days for the chromosome test results. Once euploid embryos are identified, they can be warmed and transferred to the uterus, one embryo at a time.
Storage of euploid embryos can provide patients the opportunity for fertility preservation with the intention of using the embryos years after they have been vitrified.
Steps for your Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)
- Phone consultation with your physician
- Coordinator Consultation
- Financial Consultation
- Medications (if needed)
- Embryo Transfer
Preparing for embryo transfer
On the day of the embryo transfer our patients may want to bring some music to listen to, as well as a small pillow from home and some warm socks. Patients are advised not to drink coffee or soft drinks before the transfer. The patient should let us know if they have a cold, cough or allergy, as they may need a cough suppressant. They will be asked to arrive at our clinic with their bladder at least half full as this will enable us to better visualize the uterus with the abdominal ultrasound
Luteal Phase
Progesterone supplement
In a normal fertility cycle, following ovulation, the body will produce the hormone progesterone, which serves to thicken the uterine lining and help an egg to implant and grow, thus maintaining an early pregnancy. In an IVF cycle, progesterone is taken most commonly by intra-vaginal insertion of micronized progesterone. Less commonly, women can take the progesterone by intra-muscular injection. Progesterone is continued for two weeks, when the patient receives a pregnancy test and continued when pregnant for an additional 3 weeks after the positive test.
Estrogen supplement
When women take the IVF stimulation medications, her estrogen levels will be very high at the end of the stimulation phase. They will tend to fall after the egg retrieval. In order to avoid a precipitous fall and risk early uterine bleeding, we usually prescribe Vivelle estrogen patches to keep a nice even level during the luteal phase. This estrogen is stopped at the first pregnancy test, regardless of the result.
It is very common to have light bleeding during the luteal phase. It is also common to have sensation of ‘heaviness’ or cramping in your pelvic area up to 10 days after egg retrieval. The ovaries frequently enlarge at this time.
Call our clinic anytime if there are any concerns, and contact us immediately if any of the following symptoms occur:
- Intense cramping
- Bleeding that is more than spotting
- Nausea
- Bloating
- Weight gain of more than 10 pounds in 3 days
- Fever of above 100 degrees
- Shortness of breath
- Pain
- Constipation
